djangorestframework
DRF Views
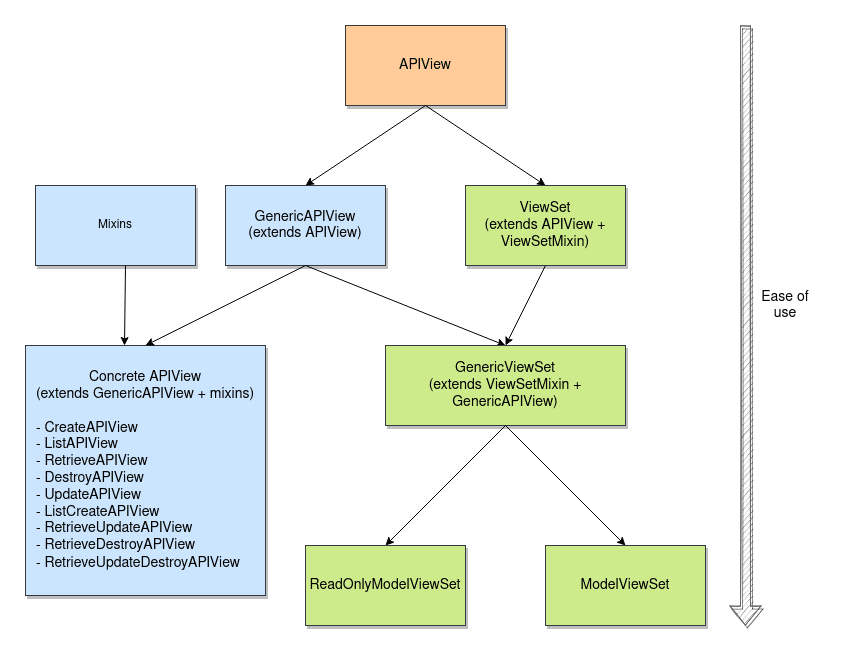
The essential component of DRF views is the APIView class, which subclasses Django's View class.
APIView class is a base for all the views that you might choose to use in your DRF application.
Whether it be-
- function-based views
- class-based views
- mixins
- generic view classes
- viewsets
they all use the APIView class.
Class-based Views
Class-based views extend the APIView class. With them, you determine how requests will be handled and which policy attributes you're going to use.
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.views import APIView
class DeleteAllItems(APIView):
def delete(self, request):
Item.objects.all().delete()
return Response(status=status.HTTP_204_NO_CONTENT)
Policy Attributes
If you want to override the default settings for your class-based views, you can use policy attributes.
In the following example, we changed the permissions and how a response is rendered with the permission_classes and renderer_classes policy attributes:
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
from rest_framework.renderers import JSONRenderer
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.views import APIView
class ItemsNotDone(APIView):
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated] # policy attribute
renderer_classes = [JSONRenderer] # policy attribute
def get(self, request):
user_count = Item.objects.filter(done=False).count()
content = {'not_done': user_count}
return Response(content)
Function-based Views
There are two ways to directly implement APIView: With a function or with a class. If you're writing a view in the form of a function, you'll need to use the @api_view decorator.
@api_view is a decorator that converts a function-based view into an APIView subclass (thus providing the Response and Request classes). It takes a list of allowed methods for the view as an argument.
from rest_framework.decorators import api_view
from rest_framework.response import Response
@api_view(['DELETE'])
def delete_all_items(request):
Item.objects.all().delete()
return Response(status=status.HTTP_200_OK)
Policy Decorators
If you want to override the default settings for your function-based view, you can use policy decorators. You can use one or multiple of the following
@renderer_classes@parser_classes@authentication_classes@throttle_classes@permission_classes
Those decorators correspond to APIView subclasses. Because the @api_view decorator checks if any of the following decorators are used, they need to be added below the api_view decorator.
from rest_framework.decorators import api_view, permission_classes, renderer_classes
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
from rest_framework.renderers import JSONRenderer
from rest_framework.response import Response
@api_view(['GET'])
@permission_classes([IsAuthenticated]) # policy decorator
@renderer_classes([JSONRenderer]) # policy decorator
def items_not_done(request):
user_count = Item.objects.filter(done=False).count()
content = {'not_done': user_count}
return Response(content)
ViewSets
A ViewSet class is simply a type of class-based View.
There are four types of ViewSets, from the most basic to the most powerful:
- ViewSet
- GenericViewSet
- ReadOnlyModelViewSet
- ModelViewSet